Comprehensive understanding of the function, classification, and applicable environment of insulators
Published time:
2021-11-12
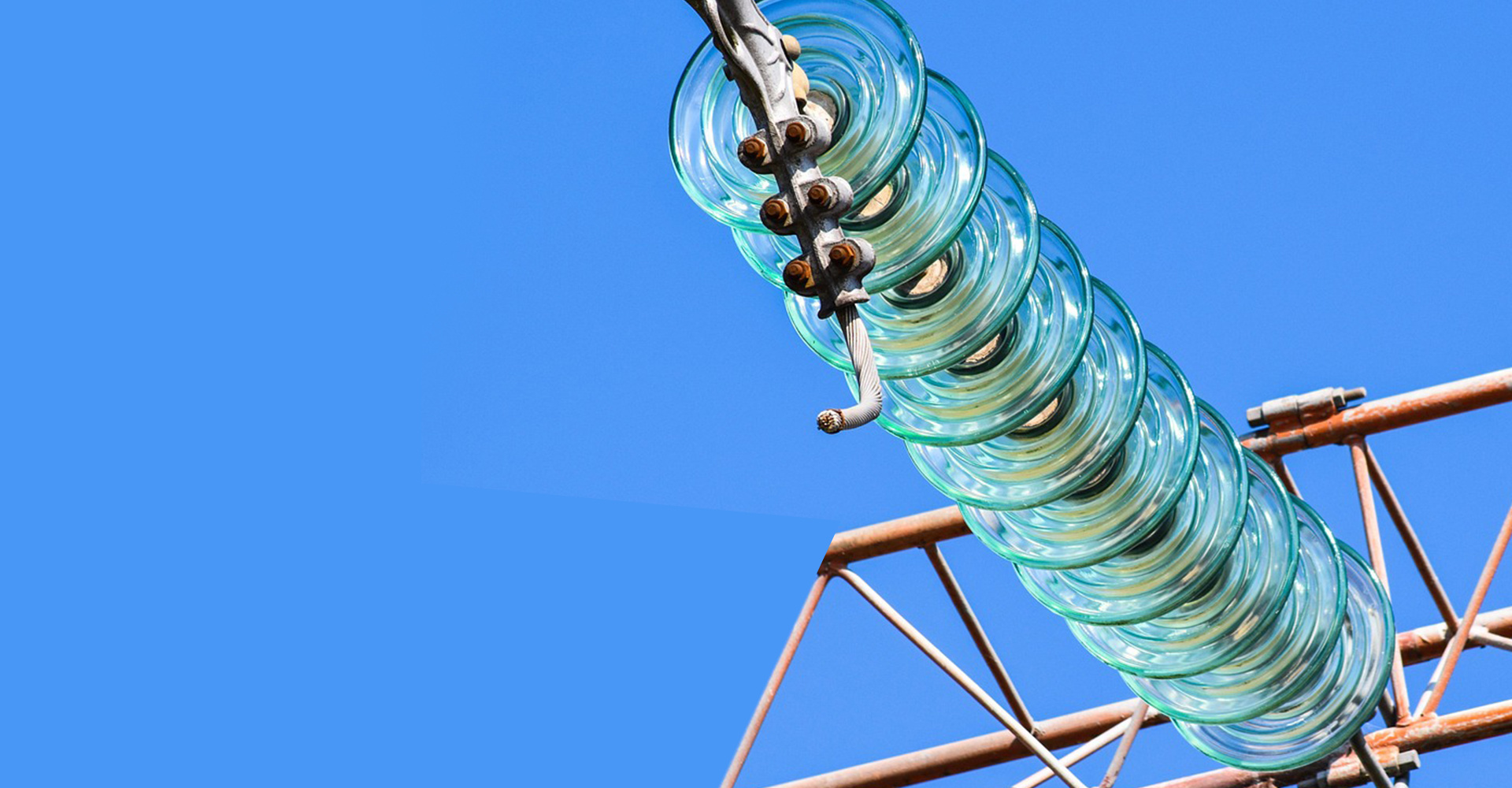
The application environment of insulator strings varies with their purpose and can be mainly divided into straight strings, jumper strings, and tension strings. In ultra-high voltage, extra-high voltage lines, and DC lines, tension insulator strings mostly use porcelain insulators and glass insulators.

The function of insulators
The name "insulator" itself reveals its core function. It is mainly used to support and suspend conductors, ensuring insulation between the conductors, towers, and ground. Insulators play an indispensable role in overhead lines of various voltage levels.
Classification of Insulators
Insulators can be classified according to different standards. Broadly, they can be divided into three categories: porcelain insulators, glass insulators, and composite insulators.
Porcelain insulators, as the earliest type with the most extensive operational experience, have made an undeniable contribution to the power industry. However, they lack hydrophobicity, unlike lotus leaves, making their surface prone to moisture and becoming wet in humid environments. To ensure the insulation performance, power employees need to regularly clean the dust and dirt from their surfaces to prevent a reduction in the insulation strength of the outer insulation surface and thus avoid flashover accidents. The maintenance cycle is usually set to 5 to 8 years.
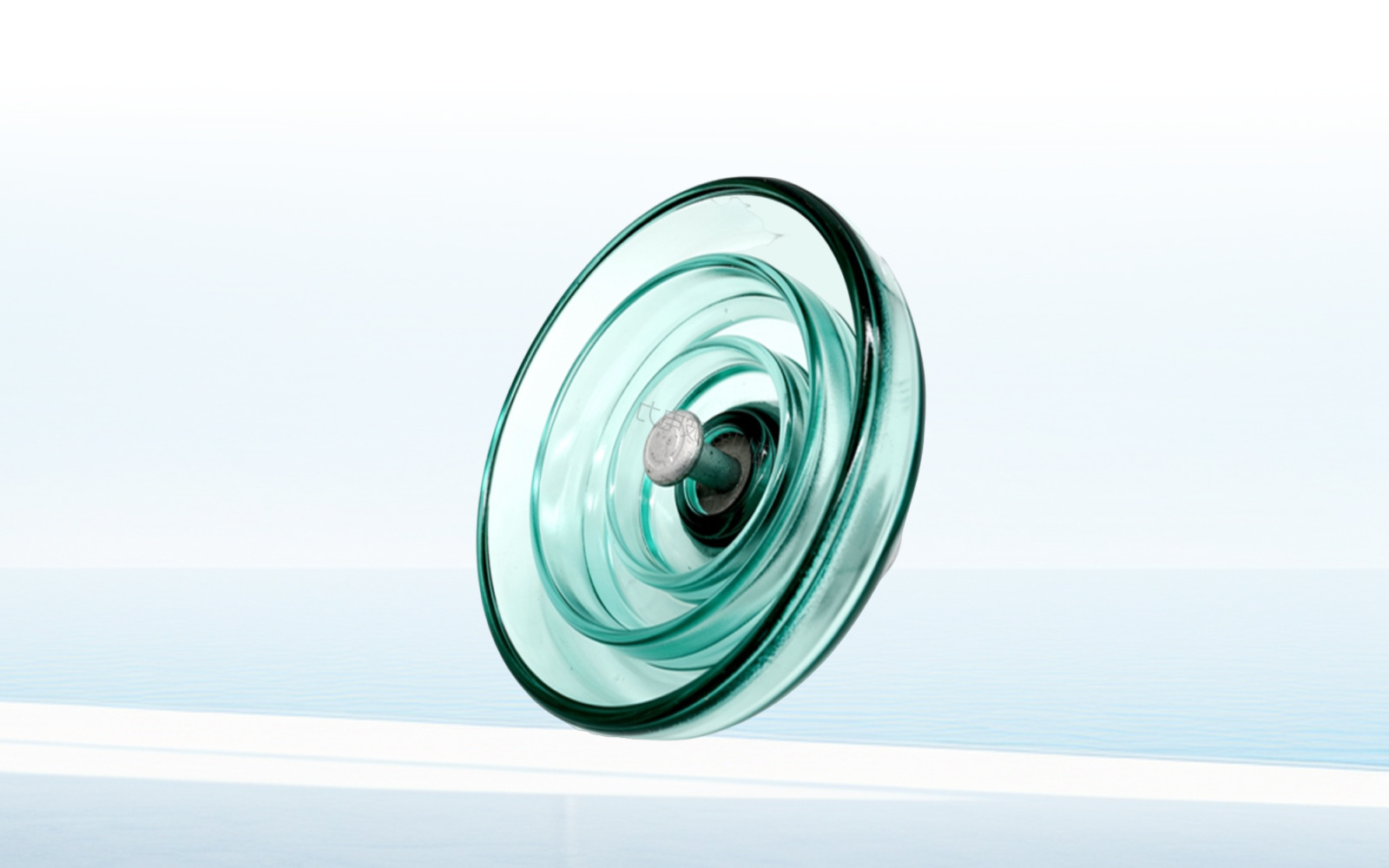
Next, we introduce glass insulators. These insulators use glass material, especially tempered glass, giving them a unique self-exploding characteristic. Once deterioration occurs, glass insulators will self-explode, a phenomenon easily identifiable by power employees, eliminating the need for specialized deterioration detection. Similar to porcelain insulators, glass insulators also lack hydrophobicity, and their surface is prone to moisture and becoming wet in humid environments. Therefore, regular cleaning is essential to maintain their surface insulation level.
Finally, we introduce composite insulators. Made of silicone rubber and core rod materials, composite insulators differ significantly from the previous two types. Their greatest advantage lies in their hydrophobicity and migration properties. Their surface cannot form a conductive water film, thus exhibiting excellent anti-flashover capabilities. Under normal operating conditions, composite insulators require virtually no special maintenance, significantly reducing maintenance costs.
Application Environment of Insulators
The application environment of insulator strings varies depending on their purpose and can be mainly divided into straight strings, jumper strings, and tension strings. In ultra-high voltage, extra-high voltage lines, and DC lines, tension insulator strings mostly use porcelain and glass insulators; while straight and jumper strings in dirty areas tend to use composite insulators. Of course, in geographically cleaner areas, some regions also use composite insulators, but porcelain and glass insulators still predominate.
Recommended News