Analysis of various types and functions of insulators
Published time:
2021-11-12
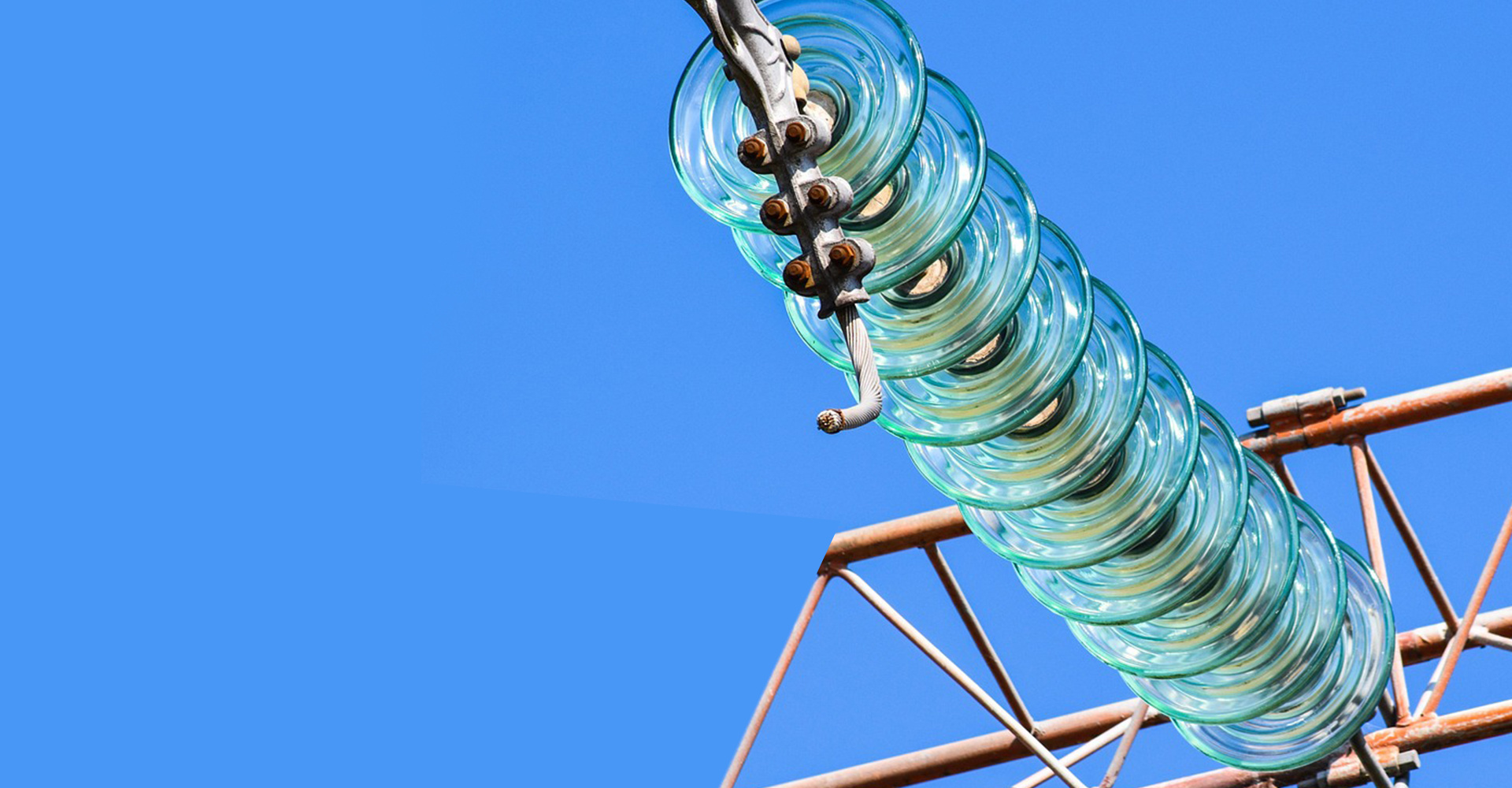
High-voltage power lines are connected to numerous disc-shaped insulators hanging on the towers. These insulators not only increase the creepage distance but also ensure the safe operation of the power system.

High-voltage power lines connect numerous disc-shaped insulators hanging on the towers. These insulators not only increase the creepage distance but also ensure the safe operation of the power system. These insulators, usually made of refined glass or ceramic, are special insulating components that play a vital role in overhead transmission lines. They are installed between conductors of different potentials or between conductors and ground potential components, capable of withstanding both voltage and mechanical stress.
With the development of society and the growth of electricity demand, the application of insulators has expanded from early telegraph poles to tall high-voltage power line towers. Creepage distance, as an important indicator of insulation performance, is particularly important in polluted areas. Depending on the degree of pollution, the insulator design needs to be adjusted accordingly to ensure its stable performance in various environments.
Insulators play two core roles in overhead transmission lines: supporting conductors and preventing current from returning to ground. To ensure the durability of these two functions, insulators must have excellent electromechanical strength to cope with changes in environmental and electrical load conditions. Any failure due to stress may damage the use and service life of the entire line.
According to different functions and structures, insulators can be divided into various types. Among them, suspension insulators are widely used in high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission lines due to their high electromechanical strength and flexible combination methods. They can not only effectively suspend or tension conductors but also ensure the insulation safety with the towers. In suspension insulators, disc and rod types are two main forms, while disc-type suspension insulators are further divided into ordinary and anti-pollution types to meet the needs of different regions and applications.
Rod-type composite suspension insulators, due to their unique advantages, play a significant role in urban power grid renovations. It can effectively utilize narrow corridors for high-voltage power transmission, not only reducing the height of towers but also contributing to saving resources and manpower. In addition, its high bending strength effectively prevents the cascading fracture accidents common in porcelain insulators, making it a superior choice unmatched by porcelain insulators.
2. Post Insulators
Post insulators play a vital role in power plants and substations. They are not only responsible for the insulation of busbars and electrical equipment but also play a role in mechanical fixation. At the same time, post insulators are also an indispensable part of electrical equipment such as isolators and circuit breakers.
According to their shape and use, post insulators can be divided into pin-type and rod-type. Pin-type post insulators, due to their unique structure, are widely used in low-voltage distribution lines and communication lines, while rod-type post insulators are more commonly used in high-voltage substations.
3. Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators are insulating devices made of electrical porcelain. This ceramic is made from quartz, feldspar, and clay, and is baked at high temperatures. Its surface is usually covered with a layer of porcelain glaze to enhance its mechanical strength, prevent water penetration, and improve surface smoothness. Among the many types of insulators, porcelain insulators are widely used due to their superior performance.
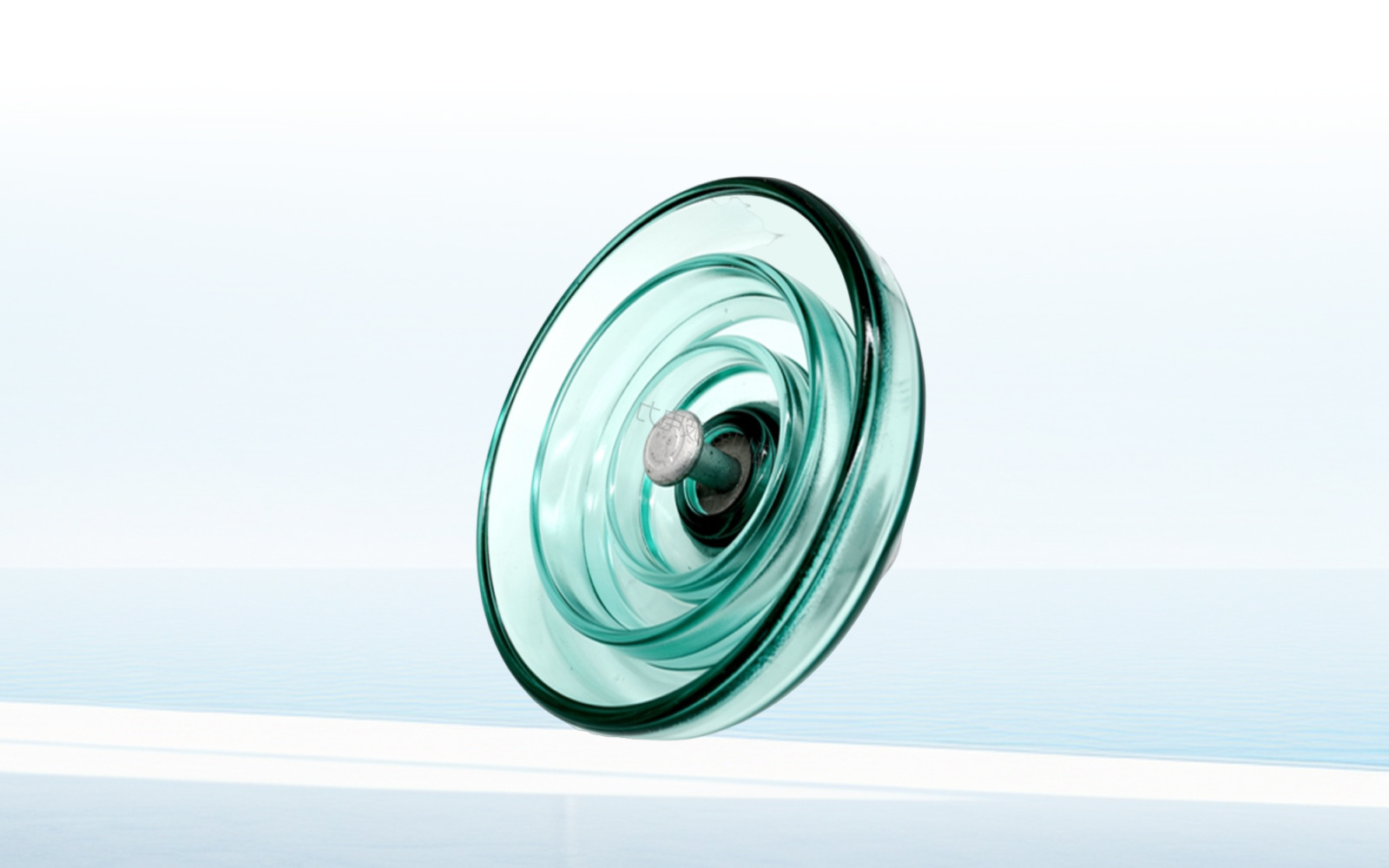
4. Glass Insulators
Glass insulators are devices made of specially tempered glass. Its surface is in a state of compressive pre-stress. Once cracks or electrical breakdown occur, the glass insulator will automatically break into small pieces, a characteristic known as "self-explosion." Because of this, glass insulators do not require "zero-value" testing during operation.
So-called zero-value insulators refer to insulators whose potential distribution at both ends is close to or equal to zero during operation. The impact of zero-value or low-value insulators on the line cannot be ignored. Due to manufacturing defects or external factors, the insulation performance of insulators will gradually deteriorate. When the insulation resistance drops to zero, the insulator is called a low-value or zero-value insulator, which is also one of the important reasons for the increase in the lightning tripping rate of the line. At the same time, the smooth surface of the insulator can reduce the capacitive reactance between the wires, thereby reducing current loss.
5. Composite Insulators
Composite insulators, also known as synthetic insulators, are composed of a glass fiber resin core rod, an organic material sheath, and a shed. It has the characteristics of compact size, light weight, and excellent tensile strength, and its anti-pollution flashover performance is also quite excellent. However, compared with porcelain and glass insulators, its anti-aging ability is slightly insufficient.
6. Low-voltage and High-voltage Insulators
Low-voltage insulators are mainly used in low-voltage distribution lines and communication lines, while high-voltage insulators are used in high-voltage, ultra-high-voltage overhead transmission lines and substations. To meet the needs of different voltage levels, different numbers of the same type of single insulators are usually used to form insulator strings or multi-section insulating columns.
7. Anti-pollution Insulators
Anti-pollution insulators increase the creepage distance by increasing or enlarging the sheds or ribs, thereby enhancing the electrical strength under polluted conditions. In addition, by changing the shape of the shed structure, the amount of natural surface fouling can be reduced, thereby improving the anti-pollution flashover performance. Its creepage distance is usually 20%~30% higher than that of ordinary insulators, or even more. In areas with frequent pollution flashovers in the Chinese power grid, double-layer shed structure anti-pollution insulators are often used. This type of insulator has strong self-cleaning ability and is easy to clean manually.
8. DC Insulators
DC insulators specifically refer to disc insulators used for DC power transmission. Compared with AC anti-pollution insulators, they have a longer creepage distance and higher volume resistivity. In addition, their connecting hardware is also equipped with sacrificial anodes to prevent electrolytic corrosion.
Next
Recommended News