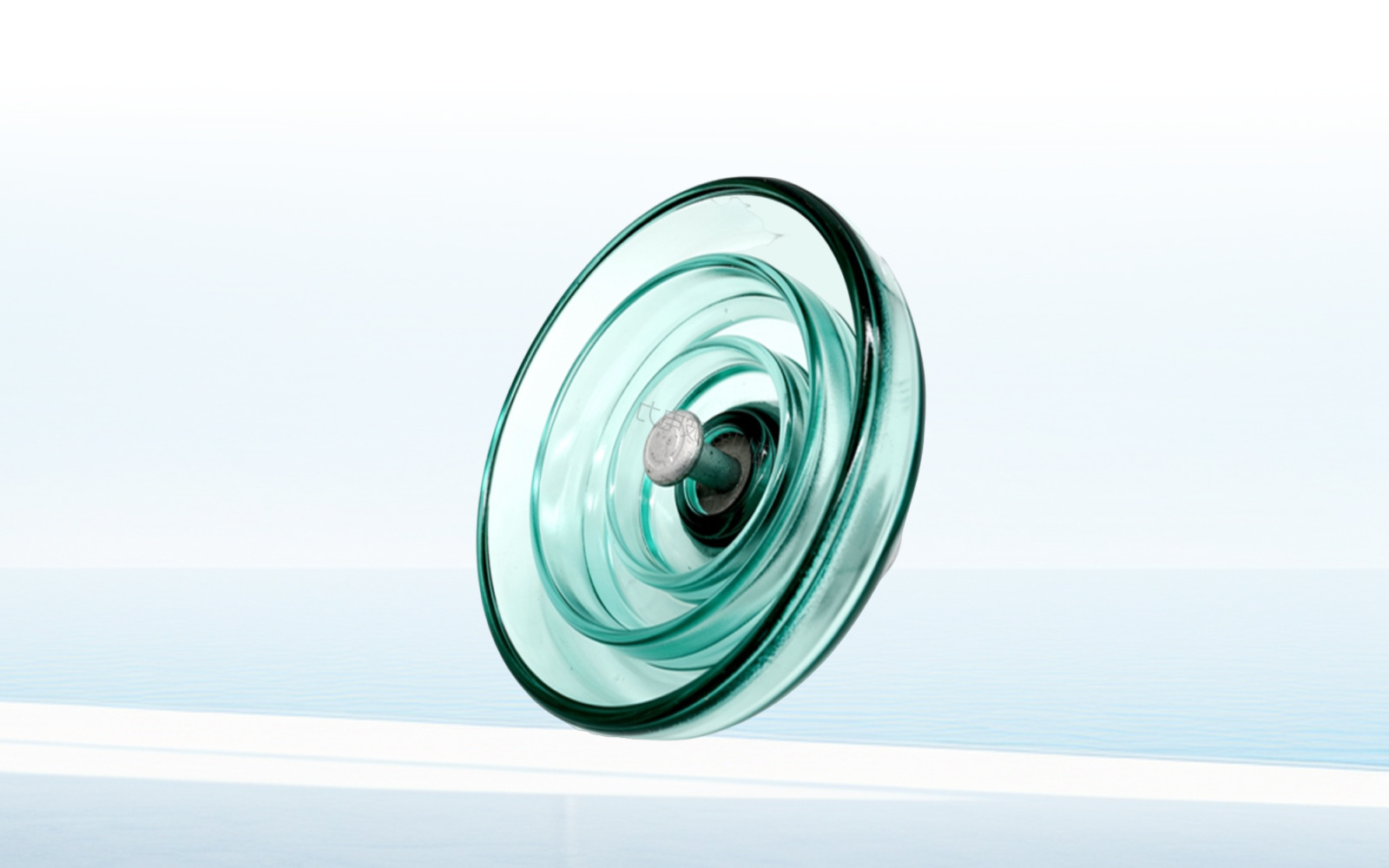
What is the function of the glass in a glass insulator?
Published time:
2021-11-12
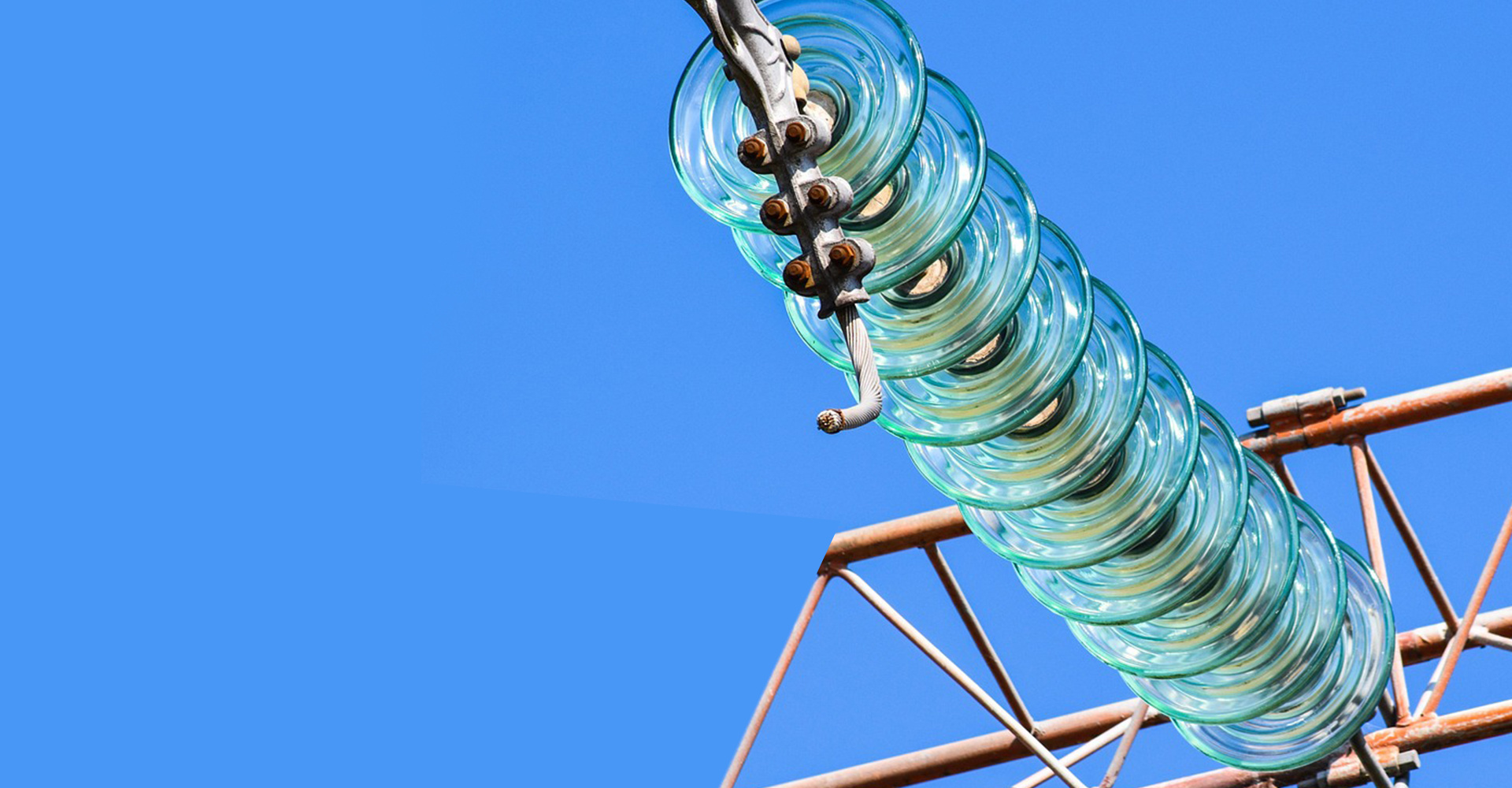
Glass insulators are commonly used high-voltage insulation components in power systems. They are used to support and fix high-voltage conductors and isolate conductors and supports with different potentials.

I. Principle of Glass Insulators
Glass insulators are commonly used high-voltage insulation components in power systems. They are used to support and fix high-voltage conductors and isolate conductors and supports with different potentials. In power systems, due to high operating voltage and harsh environments, insulators are required to have good insulation performance and durability.
The insulation principle of glass insulators is gas insulation and surface insulation. Glass insulators consist of a shell, metal feet, insulating materials, etc., where the insulating material is glass, which can effectively isolate the environment around electrical equipment and conductors, preventing leakage and electric shock accidents.
II. The Role of Glass in Glass Insulators
Glass, as the main material of glass insulators, plays an important role in its design and manufacturing. Glass has excellent electrical insulation, mechanical properties, and chemical stability, and can withstand high voltage, high temperature, and high humidity complex environments, ensuring the long-term stable operation of the insulator.
Specifically, the role of glass in glass insulators includes:
1. Electrical Insulation: Glass has good dielectric strength and insulation properties, which can effectively prevent current from flowing through the surface of the insulator, preventing leakage and electric shock accidents.
2. Mechanical Support: Glass insulators need to support and fix high-voltage conductors and other equipment in the power system. Glass, as the main material of the insulator, has good mechanical strength and hardness, and can withstand external forces to ensure equipment stability.
3. Chemical Stability: Glass can maintain stability in harsh environments such as acids, alkalis, high temperatures, and high humidity, and will not be damaged by oxidation or corrosion, maintaining insulation performance for a long time.
III. Classification and Application Fields of Glass Insulators
According to different structures and uses, glass insulators can be divided into glazed glass insulators, post-type glass insulators, composite insulators, and other types. The application fields mainly cover power systems, electrified railways, urban rail transit, photovoltaic/wind power generation, etc., and are widely used in high-voltage transmission lines, converter substations, switchgears, and distribution devices.
In summary, glass, as the main material of glass insulators, plays an important role in the insulation, mechanical support, and chemical stability of insulators. Glass insulators, due to their good insulation performance and durability, are widely used in power systems and electrical equipment, ensuring the stable and safe operation of the power system.
Recommended News